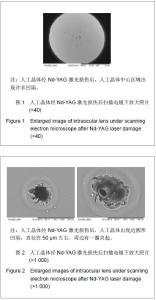
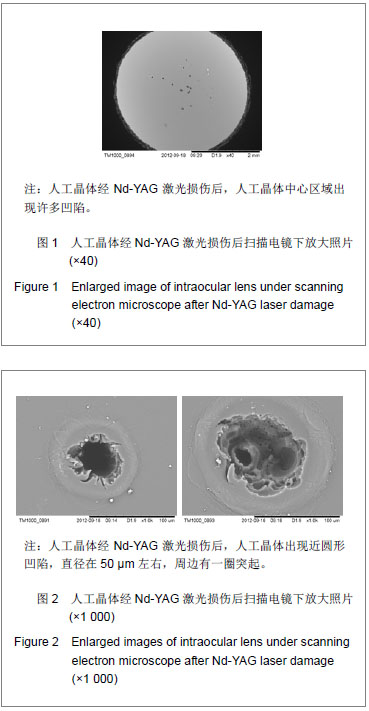
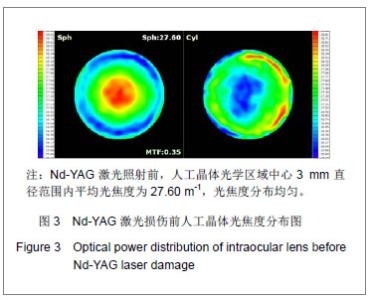
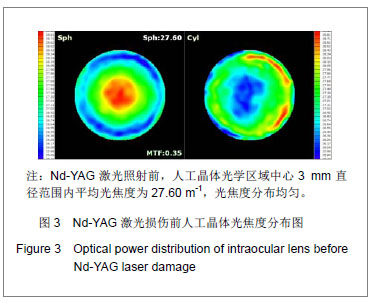
| [1]Livingston PM, Carson CA, Taylor HR.The epidemiology of cataract: a review of the literature.Ophthalmic Epidemiol.1995; 2(3):151-164.[2]林振德,李绍珍.小切口白内障手术[M].北京:北京人民卫生出版社,2002:98-100.[3]Kohnen T.Multifocal IOL technology: a successful step on the journey toward presbyopia treatment.J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008;34(12):2005.[4]Keates RH, Sall KN, Kreter JK.Effect of the Nd-YAG laser on polymethylmethacrylate, HEMA copolymer, and silicone intraocular materials.J Cataract Refract Surg.1987;13(4): 401-409.[5]Capone A Jr, Rehkopf PG, Warnicki JW, et al.Temporal changes in posterior capsulotomy dimensions following neodymium:YAG laser discission.J Cataract Refract Surg. 1990;16(4):451-456.[6]Lundqvist B, Mönestam E.Ten-year longitudinal visual function and Nd: YAG laser capsulotomy rates in patients less than 65 years at cataract surgery.Am J Ophthalmol.2010; 149(2):238-244.[7]高丽芬,陈薇,李建平,等.Nd:YAG激光致各种人工晶体损伤临床观察[J].山东医药,2000,40(15):14-15.[8]王又冬,张劲松,张洋.NdxivYAG激光对不同材料人工晶体损伤作用的实验研究[J].中华眼科杂志,1998,34(2):103-105.[9]沈念慈,王诚忠.YAG激光致人工晶体损伤[J].中国实用眼科杂志, 1995,13(8):502-503.[10]刘增业.Nd:YAG激光损伤人工晶体一例[J].眼科,1995,4(2):127.[11]张建东.Nd:YAG激光致人工晶体混浊2例[J].中国实用眼科杂志, 2004,22(8):595.[12]穆璀平,曹文兵.小瞳孔下Nd:YAG激光治疗人工晶体植入后囊膜混浊的观察[J].宁夏医学杂志,2006,28(2):149-150.[13]吴艺,古爱平,夏朝霞.着色聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯人工晶体在白内障及角膜移植三联术中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(3):537-540.[14]张晓鸣,汪素萍.四襻式亲水性丙烯酸折叠式人工晶体植入术后临床观察[J].海南医学,2008,19(10):34-35.[15]张红言,施玉英.人工晶体材料的不同与后囊混浊关系的探讨[J].国外医学眼科学分册,2002,24(1):51-54.[16]Ursell PG, Spalton DJ, Pande MV, et al.Relationship between intraocular lens biomaterials and posterior capsule opacification.J Cataract Refract Surg.1998;24(3):352-360.[17]孙炜.Nd.YAG激光对蓝光滤过性折叠式人工晶体损伤作用的实验研究[D].辽宁:中国医科大学,2006:4.[18]曾思明.不同焦点掺钕-钇铝石榴石(ND:YAG)激光治疗对人工晶体损伤的观察[J].广西医学,2004,26(4):555-556.[19]Trinavarat A, Atchaneeyasakul L, Udompunturak S.Neodymium:YAG laser damage threshold of foldable intraocular lenses.J Cataract Refract Surg.2001;27(5): 775-780.[20]谢立信.IOL植入学[M].第2 版.北京:人民卫生出版社,1997: 243-244.[21]Owsley C, Stalvey BT, Wells J, et al.Visual risk factors for crash involvement in older drivers with cataract.Arch Ophthalmol. 2001;119(6):881-887.[22]Auffarth GU, Hunold W, Hürtgen P, et al.Night driving capacity of pseudophakic patients.Ophthalmologe.1994;91(4): 454-459. |